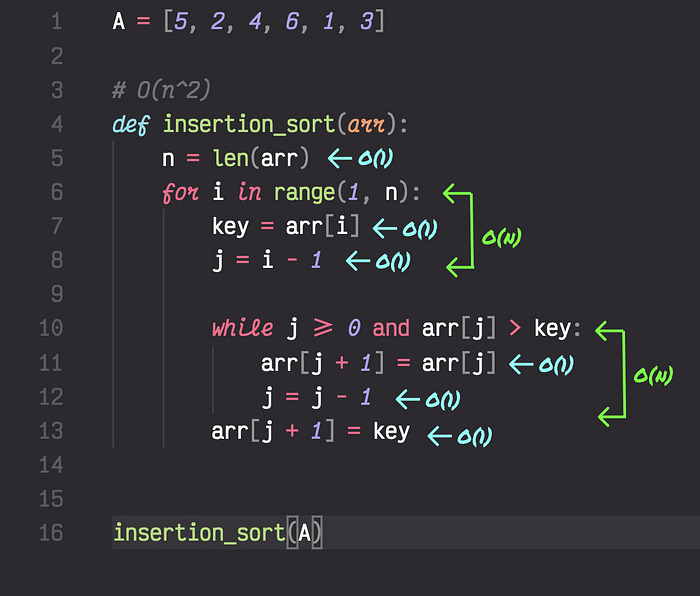
The world of Flutter app development is ever-evolving, offering a plethora of templates that make the job of developers easier and more efficient. Whether you’re an aspiring Flutter developer or an experienced one, these templates will undoubtedly add value to your work. Here, we’re going to explore the 10 best FlutterFlow app templates in 2023 that have the potential to accelerate your project’s development time and provide a smooth user experience.

Here are the top 10 FlutterFlow app templates that are shaping the mobile app landscape in 2023
Light Themed E-commerce App

Ignite your e-commerce business with our Light Themed E-commerce App template designed specifically for FlutterFlow! This template offers a simple, visually appealing, and impactful design, enhancing the shopping experience for your customers. 🌟 Features:
📱 Simple and user-friendly e-commerce UI
🌈 Light theme for an appealing visual experience
💥 Impactful design to engage and retain users

Presenting Eventor — an advanced event details and ticketing screen template for FlutterFlow. Built with a stack structure and integrated with Mapbox, Eventor offers an intuitive event details page and a ticket barcode feature, streamlining the ticketing process for any event. 🎫 Features:
📐1️⃣ Stack Structure: Utilize the highly versatile stack structure for a smooth and responsive user interface.
🌐2️⃣
Mapbox Integration: Enhance user experience with integrated Mapbox
functionality, providing real-time location updates for events.
📅3️⃣
Event Details Page: Offer comprehensive event details in a neat and
attractive layout, ensuring users have all the information they need.
🔖4️⃣
Ticket Barcode Feature: Simplify the ticketing process with an
integrated ticket barcode feature, allowing users to keep track of their
tickets digitally.
How to Use:
Implement the Eventor template in your project to offer an enriched event experience, complete with detailed information and seamless ticketing.

Unleash the power of dynamic menu animation with our FlutterFlow Animated Menu App Template. Built on the robust foundation of page state, this template employs the versatility of stacks to bring alive the menu and content animation. Modify the background content as per your needs by updating the page component in the background. Though it’s designed as a single-page template, it’s equipped with components and app state settings, thereby functioning as an app. 😎 Features:
🎨1️⃣ Dynamic Menu Animation: Leverage the power of stacks to create lively animations for your menu and content.
🔄2️⃣
Background Content Modification: Adapt the background content to your
project’s needs by updating the page component in the background.
📃3️⃣
Single Page Design: Although designed as a single page, it functions as
an app due to the inclusion of components and app state settings.
💡4️⃣
Ease of Use: Download this app, copy the page to your project, and
voila — you’re all set. Please remember to remove the background
component (component with graph and list) before copying the page.
🚀5️⃣ Menu Animation Trigger: The menu animation is set to trigger on a page state boolean “showMenu”.
How to Use:
Simply download this app and copy the page to your project. Be sure to remove the background component (component with graph and list) prior to copying the page. It’s crucial to copy the page as the menu animation is activated via a page state boolean called “showMenu”.

Unleash your creativity with our AI Artistry App, an innovative social media app template powered by FlutterFlow and Replicate. By merely typing an image description, users can witness the magic of Replicate’s ML model transforming their words into stunning visuals.
Features:
📝 User-friendly interface for entering image descriptions
🎨 AI-powered generation of beautiful images based on user input
🔄 Responsive app design for seamless user experience
How to Use:
1️⃣ Create a Replicate account and generate an API key
2️⃣ Retrieve your API key and navigate to the API calls section
3️⃣ Paste the API key in the Header section of each where it says API_KEY_HERE
4️⃣ Enjoy transforming your words into beautiful images!

Welcome to KayakFlow, an immersive kayak rental app template crafted meticulously for a seamless user experience. Complete with cutting-edge functionalities and integrated animations, KayakFlow is perfect for businesses looking to streamline their rental services.
Features:
🛶 Detailed kayak listings for informed decisions
🔄 Integrated animations for a dynamic user experience
🛒 Smooth rental and checkout process
How to Use:
1️⃣ Select your preferred kayak from the detailed listings
2️⃣ Rent your kayak with just a few taps
3️⃣ Proceed to checkout to finalize your rental process
4️⃣ Enjoy your kayaking adventure!

Presenting AgileFlow, a responsive Kanban Board App Template designed with the robust capabilities of FlutterFlow. Experience superior project management with this intuitive app that allows for task organization into customizable columns, and easy project prioritization across various devices.
Features:
🔄 Responsive design for seamless use on any device
📝 Customizable columns for task organization
🚀 Prioritize projects with a simple drag-and-drop interface
🔒 Firebase integration for secure and reliable data storage
How to Use:
1️⃣ Clone this project into your FlutterFlow workspace
2️⃣ Connect to your Firebase account for data management
3️⃣ Your customized Kanban Board App is ready to boost productivity!

Unleash your creativity with the Sketch-to-Image FlutterFlow x Replicate App Template! Draw your vision and let Replicate’s advanced ML model transform it into a stunning image. Perfect for artists, designers, and anyone who wants to visualize their ideas quickly and easily.
Features:
✏️ User-friendly sketching interface
🧠 Powered by Replicate’s ML model
🖼️ Instantly transforms sketches into images
🔄 Quick and easy setup
How to Use:
1️⃣ Create a Replicate account and generate an API key
2️⃣ Clone this template into your FlutterFlow project
3️⃣ Paste your API key in the “Replicate API” group where it says
4️⃣ Your Sketch-to-Image app is ready to bring your visions to life!
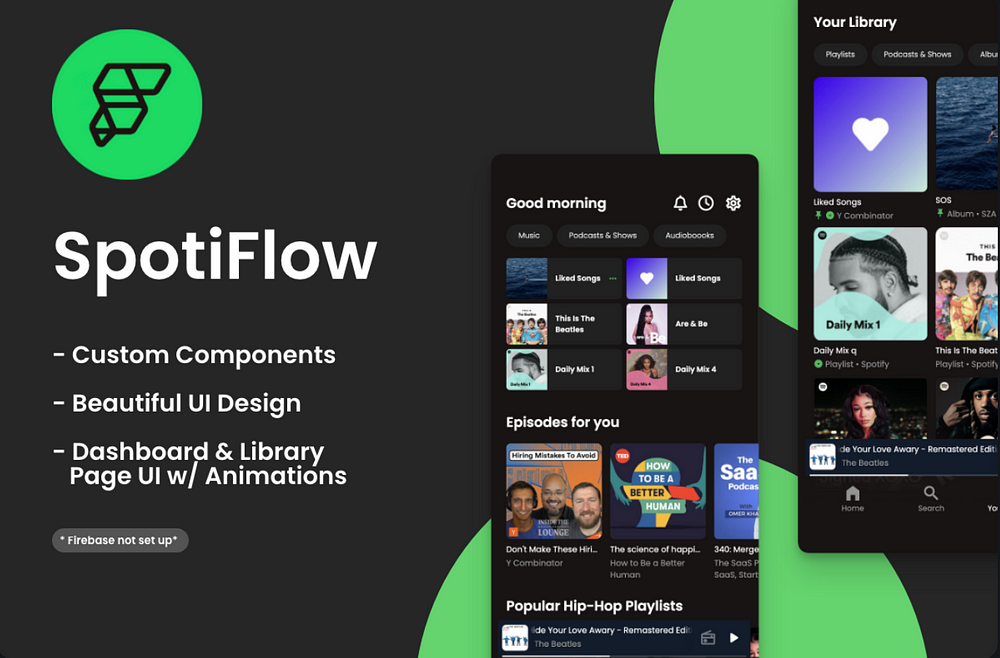
Jumpstart your custom music app development with SpotiFlow, a Spotify-inspired UI template with components and features built specifically for FlutterFlow! With this template, you can quickly utilize the pre-built UI for the Dashboard and Library page, paving the way to your ideal music app UI. Set up Firebase, add notifications, and kickstart your app in no time! How to Use:
🔥 Please note, Firebase integration is not included — you’ll need to set up Firebase according to your preferred architecture to use this within an app. This template includes the UI components/animations and navigation for a seamless development experience.
Features:
🎶 Spotify-inspired UI components for a familiar user experience
📊 Pre-built UI for Dashboard and Library page for quick setup
🔔 Add notifications to keep users engaged
🔧 Easy setup with Firebase for robust backend support
🔄 Seamless navigation for an enhanced user experience

Elevate your music app development with Flowtify, a fully functional template based on Soroush Norozy’s Spotify Redesign UI, tailored for FlutterFlow. This template features a responsive design, mesmerizing animations, and a sleek, modern interface, providing an ideal starting point for your next music app project. 🌟 Features:
📱 Ready-to-use template with a responsive design that seamlessly adapts to any screen size
✨ Eye-catching animations that add a dynamic flair to your app
🚀 Quick and easy setup for a streamlined development process
Flowtify is a perfect fit for developers, designers, and entrepreneurs seeking a turnkey solution to create a unique and engaging music app. With its ready-to-use design, you can launch your app swiftly and concentrate on scaling your business. Try Flowtify today and elevate your music app experience! How to Use:
🚀 Launch your music app in no time using our sleek, modern interface and responsive design.

Supercharge your automotive app development with our Tesla App template, perfectly designed for FlutterFlow. This template mimics the stunning, user-friendly interface of the renowned Tesla app, providing a seamless experience for users. Whether you’re creating an app for electric vehicles or traditional ones, this template provides a strong foundation with its intuitive navigation, sleek design, and comprehensive vehicle management features. 🌟 Features:
- 🔋 Electric vehicle management features
- 🌐 Intuitive navigation for easy access to features
- 🎨 Sleek design inspired by Tesla’s own app
- 🚀 Ideal for electric and traditional automotive apps
How to Use:
1️⃣ Clone the template into your FlutterFlow project
2️⃣ Customize the features and design to suit your vehicle range and branding
3️⃣ Your personalized Tesla-like app is ready to impress your users!

Harness the power of healthy living with our Health & Fitness App template, specifically designed for FlutterFlow. This template features a robust array of tools such as exercise tracking, meal planning, goal setting, and progress monitoring, making it an ideal solution for fitness enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals. Its sleek design and user-friendly interface make it perfect for developers aiming to create engaging and effective health and fitness apps. 🌟 Features:
🏋️♀️ Exercise tracking for workout management
🍽️ Meal planning for nutritional guidance
🎯 Goal setting to keep users motivated
📈 Progress monitoring for tracking improvements
🎨 Sleek design for a visually appealing user experience
👆 Easy-to-use interface for seamless navigation
Chat GPT — Industry Prompter App

Craft a personalized user experience with our Chat GPT — Industry Prompter App template, specifically designed for FlutterFlow. This simple yet powerful app lets you generate initial prompts tailored to your users’ needs. While it currently features a marketing plan example, its flexibility allows adaptation to any industry with ease. Expand and customize it to suit your unique requirements! How to Use:
1️⃣ Copy the template into your FlutterFlow project
2️⃣ Customize the prompt content to align with your industry needs
3️⃣ Expand and enhance the features as needed
4️⃣ Your personalized Industry Prompter App is ready to engage your users!
Features
🎯 Creates industry-specific initial prompts for enhanced user experience💡 Versatile design allows application to any industry
🔧 Easily expandable and customizable to match your unique needs
🚀 Quick and easy setup for a fast-paced development process
Flutter Flow marketplace provided by code.market
Are you a developer skilled in FlutterFlow? Do you have a knack for creating brilliant and functional templates? If so, code.market could be the FlutterFlow marketplace for you to not only share your work with the world but also earn income from your creations.
Reference
https://cdmrkt.medium.com/the-10-best-flutterflow-app-templates-in-2023-80151c0c4ace